nLab linearly distributive category
Context
Monoidal categories
With braiding
With duals for objects
-
category with duals (list of them)
-
dualizable object (what they have)
-
ribbon category, a.k.a. tortile category
With duals for morphisms
With traces
Closed structure
Special sorts of products
Semisimplicity
Morphisms
Internal monoids
Examples
Theorems
In higher category theory
Contents
- Idea
- Definition
- Examples
- Linear functors and transformations
- Related structures
- Mix, isomix and compact linearly distributive categories
- Star-autonomous category
- Polycategories
- Symmetric monoidal categories
- Linear bicategories
- Internal structures
- As lax Frobenius algebras
- History
- Related pages
- References
Idea
A linearly distributive category is a category with two monoidal structures (“times”) and (“par” written as in linear logic) that “distribute” in the sense that there is a map (not necessarily invertible)
Linearly distributive categories are the “representable” form of polycategories, and they are also what “remains” of a star-autonomous category when the involution is forgotten but the dual tensor is remembered.
Another way to say essentially the same thing is that a -autonomous category is like a compact closed category in which the unit and counit of the dual objects refer to two different tensor products: we have but , where and are two different monoidal structures. A linearly distributive category encodes the necessary relationship between two such monoidal structures such that this makes sense, i.e. such that the triangle identities can be stated.
Definition
A linearly distributive category (also called a weakly distributive category) is a monoidal category in two ways, with monoidal structures and equipped with extra associator natural transformations
and the obvious six pentagon equations and four triangle equations that make the monoidal structures work together nicely (Cockett-Seely 1997). (Some of these equations can be interpreted as saying that the s are tensorial strengths for the functors and with respect to the monoidal structure.) A symmetric linearly distributive category is one in which both monoidal structures are symmetric and three squares commute relating the symmetries to the s.
These extra associators are sometimes called “distributors”, and should not be confused with profunctors. The term is a pun on the distributivity of multiplication over addition, but “linearized” so that each variable only appears once in the result.
In a symmetric LDC, the symmetry maps induce the following permuting distributivity maps:
An LDC which is equipped with all the four linear distributivity maps is said to be non-planar.
Warning: a distributive category cannot be made into a linearly distributive category with and unless it is a partial order (but every distributive lattice is indeed a linearly distributive category) (for a proof, see Cockett-Seely 1997). This mistake is easy to make and even appears in print in one or two places.
Examples
-
Any star-autonomous category is linearly distributive, with . See that page for many examples of this.
-
Any distributive lattice is linearly distributive, with and . (This does not extend to distributive categories.)
-
Any monoidal category is linearly distributive trivially with .
-
If is an invertible object in a monoidal category, then defining yields a linearly distributive structure whose linear distributors are isomorphisms.
-
The category of modules for a bialgebra in any linearly distributive category (hence, in particular, in any star-autonomous category) is again linearly distributive. It is generally only star-autonomous if the bialgebra is a Hopf algebra.
Linear functors and transformations
A linear functor between linearly distributive categories consists of a pair of functors such that, is a lax monoidal functor with respect to , is a colax monoidal functor with respect to , and there are “linear strengths”
satisfying appropriate coherence conditions (Cockett-Seely 1999). A linear natural transformation consists of a monoidal transformations and satisfying further coherence conditions. This defines a 2-category of linearly distributive categories, which has the property of embedding the 2-category of -autonomous categories and arbitrary lax monoidal functors (see below).
On the other hand, a linear functor in this sense is more general than a functor between underlying polycategories (see below). The latter probably coincide with linear functors having the property that as functors (so that the same functor is -lax monoidal and -colax monoidal) and the linear strengths are identities. We might call these Frobenius linear functors, since such a is the same as a Frobenius algebra in , and when specialized to the monoidal case they coincide with Frobenius monoidal functors.
Yet stronger is the notion of strong Frobenius linear functor, in which the lax and colax monoidal structures are strong.
Related structures
Mix, isomix and compact linearly distributive categories
There are a series of structural steps by which linearly distributive categories collapses to a monoidal categories as shown in the picture below.
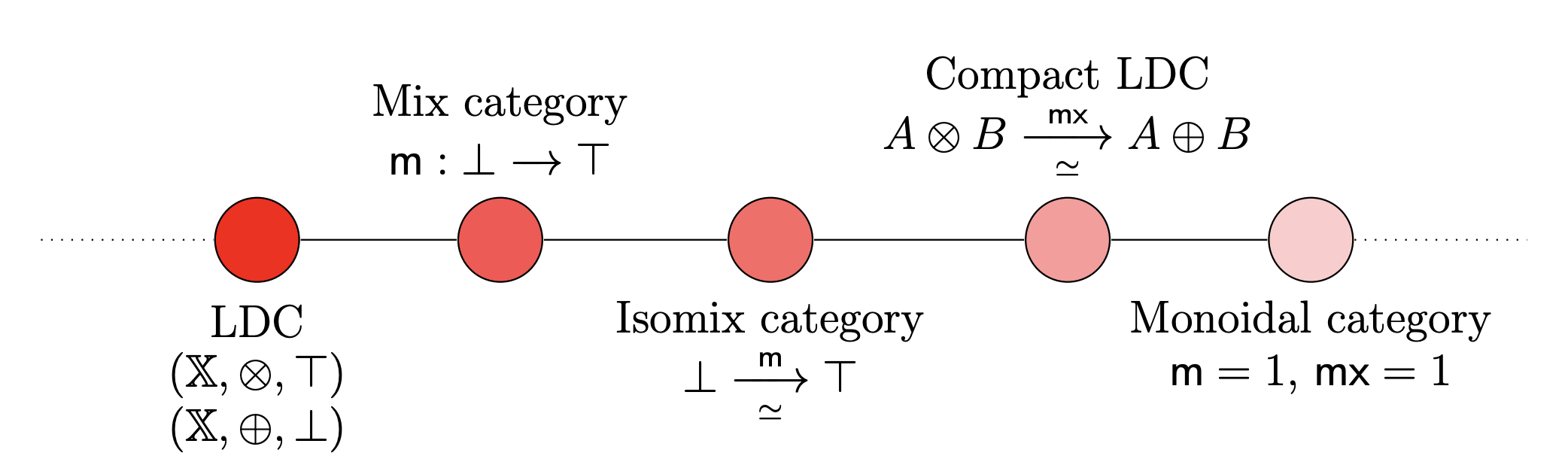
A mix category is an LDC with a mix map , and a such that:
1) The following diagram commutes
2) The map, , called the mixor is natural in both the arguments.
An isomix category is a mix category in which the mix map is a natural isomorphism, .
In an isomix category, the mixor is automatically a natural transformation. The mix map being an isomorphism does not imply that the mixor is a natural isomorphism.
An isomix category in which the mixor is a natural isomorphism is a compact LDC. The term “compact” here refers to the fact that both the monoidal structures are isomorphic. All compact LDCs are linearly equivalent to the underlying monoidal categories on the tensor and the par .
Star-autonomous category
Any star-autonomous category has an underlying symmetric linearly distributive category where we define , or equivalently , where is the internal-hom. The left distributor, for instance, is obtained as follows:
Conversely, we say that a symmetric linearly distributive category with monoidal structures and has a negation if every object has a dual and arrows
subject to triangular equations
Then symmetric linearly distributive categories with negations are the same as -autonomous categories; see (Cockett-Seely 1997). Moreover:
-
the forgetful functor from -autonomous categories to symmetric linearly distributive ones has a left adjoint that “freely adjoins negations”. I don’t know which kind of functors this statement refers to, but it’s probably strong Frobenius ones.
-
This functor also has a right adjoint that picks out (in the linear sense) the “nucleus” of dualizable objects (Cockett-Seely 1999). This adjunction uses lax monoidal functors between -autonomous categories and linear functors between linearly distributive categories.
-
Analogous facts hold relating non-symmetric linearly distributive categories with non-symmetric star-autonomous categories?.
Polycategories
Any linearly distributive category has an underlying polycategory where we define to be . The polycategorical compositions are obtained using the distributors. For instance, we should be able to compose with to get ; in a linearly distributive category this is the composite
Conversely, a polycategory that is suitably “representable” yields a linearly distributive category. Also, the forgetful functor from linearly distributive categories and strong Frobenius linear functors to polycategories has a left adjoint (Cockett-Seely 1997).
Symmetric monoidal categories
Any symmetric monoidal category becomes a linearly distributive category in which both monoidal structures are the same; all the required structure and coherence conditions follow straight from coherence for symmetric monoidal categories. Note that such examples are almost never star-autonomous.
These examples satisfy the extra property that the distributors are isomorphisms. However, not every linearly distributive category in which the distributors are isomorphisms are of this form; the rest are “shifted monoidal categories” in which , where is a chosen -invertible object.
Linear bicategories
Linear bicategories are a horizontal categorification of linearly distributive categories (Cockett-Koslowski-Seely 1999).
Internal structures
Some structures normally defined in a monoidal category can more generally be defined in a linearly distributive category. This includes dual objects (yielding the above “negations”) and also Frobenius algebras (Egger 2010).
As lax Frobenius algebras
Linearly distributive categories that are both closed and co-closed can be identified with lax Frobenius algebras in the polycategory MVar? of multivariable adjunctions; see this blog post.
History
A key feature of linearly distributive categories is the existence of morphisms of the form
which exhibit linear distributivity. The importance of this map had previously been overlooked in the linear logic community due to the (continuing) tendency to write sequents in a one-sided manner. However, the importance of the map was eventually realized by a number of people, albeit usually in the case of posets. Cockett-Seely 1997 referred to Lambek 1993 for a survey of some of those developments.
This concept was called a weakly distributive category when it was presented by Robin Cockett and Robert Seely at the 1991 Durham LMS symposium on applications of categories in computer science (Cockett-Seely 1992 and Cockett-Seely 1997). Independently, Valeria de Paiva, a student of Martin Hyland, also presented this concept in her PhD thesis as the category , and credited conversations with Jean-Yves Girard at a 1987 Boulder conference for inspiring the construction. (de Paiva 1991)
Subsequently, in recognition of the concept’s fundamental role in the categorical semantics for the proof theory of linear logic, and the fact that such categories are not a “weakening” of distributive categories in any standard sense, these categories were called linearly distributive categories.
Linearly distributive categories allowed the modularization of the proof theory of linear logic and a more systematic approach to the then unsolved coherence problems associated with the units in linear logic. This program of work culminated in a solution which was published in (BCST 1996)
These techniques also solved a classical open problem in closed monoidal categories concerning the behaviour of the triple dual. Todd Trimble, who was completing his PhD. at the time, provided a vital insight to the group on how this problem could be solved and this unlocked the solution to the general problem.
Linearly distributive categories are to polycategories as monoidal categories are to multicategories. Namely, when one represents “the commas” of a polycategory one obtains a linearly distributive category. Crucially, the key coherence issues of (the multiplicative fragment of) linear logic concerning the units is already present at the linearly distributive level – but it is no longer cluttered by the other features of linear logic. Thus, this provided a clean substrate from which to study and isolate this coherence problem.
Contrary to the general direction of work in coherence (and, indeed, in the linear logic community), the solution to the problem, which was given in (BCST 1996), involved an expansion reduction rewriting system modulo equations. At that time, the prevailing proof theoretic strategy for solving coherence problems was simply to cut-eliminate: usually this suffices to leave proofs in a normal form. However, this system was notable as this strategy clearly failed: it was necessary to leave some equations in the system. These equations, of course, involved the possible “rewiring”s of the units.
At that time this was generally thought to be a rather unsatisfactory and unnecessarily technical solution especially when compared to the normal forms to which the community was accustomed. However, in 2014, Willem Heijltjes and Robin Houston (HH2014) showed that equality of morphism is a PSPACE?-complete problem. This essentially implies that there is no practical way round this problem beyond a search of the rewiring equivalence class.
Linearly distributive categories have now been used as the substrate for a number of systems.
Related pages
-
A linearly distributive category in which the units of the two monoidal structures coincide is an (iso-)mix category.
References
-
M.E. Szabo, Polycategories, Comm. Algebra 3 (1975) 663-689. (doi)
-
Valeria de Paiva, The Dialectica categories, University of Cambridge Technical Report UCAM-CL-TR-213, 1991. (pdf)
-
Robin Cockett, Robert Seely, Weakly Distributive Categories, in M.P. Fourman, P.T. Johnstone, A.M. Pitts, eds., Applications of Categories in Computer Science, London Mathematical Society Lecture Note Series 177 (1992), pp. 45–65. (book website)
-
Joachim Lambek, From categorial grammar to bilinear logic, in Kosta Dosen and Peter Schroder-Heister, eds., Substructural Logics, Clarendon Press, 1993, pp. 207–237. (book website)
-
R. Blute, J.R.B. Cockett, R.A.G. Seely, T. Trimble, Natural deduction and coherence for weakly distributive categories, J. Pure Appl. Algebra, 113 (1996), pp. 229–296. (web)
-
Robin Cockett, Robert Seely, Weakly Distributive Categories, J. Pure Appl. Algebra, 114 (1997) 2, pp 133-173. (corrected version: ps.gz, pdf)
-
Robin Cockett and Robert Seely, Linearly distributive functors, J. Pure Appl. Algebra 143 (1999), pp. 155–203. (doi)
-
Paul-André Melliès, Categorical Semantics of Linear Logic, published in Pierre-Louis Curien, Hugo Herbelin, Jean-Louis Krivine, Paul-André Melliès. Interactive models of computation and program behaviour, Panoramas et Synthèses 27, Société Mathématique de France, 2009.
-
Willem Heijltjes, Robin Houston, No proof nets for MLL with units: proof equivalence in MLL is PSPACE-complete, CSL-LICS ‘14 Proceedings of the Joint Meeting of the Twenty-Third EACSL Annual Conference on Computer Science Logic (CSL) and the Twenty-Ninth Annual ACM/IEEE Symposium on Logic in Computer Science (LICS), Article No. 50. (web)
-
Robin Cockett, Jürgen Koslowski?, Robert Seely, Introduction to linearly distributive categories, Mathematical Structures in Computer Science, Vol. 10, 2000 pp 165-.203 pdf
-
Robin Cockett and R.A.G. Seely, 1997. Proof theory for full intuitionistic linear logic, bilinear logic, and mix categories. 1997. TAC 5:3. Web.
Frobenius algebras in linearly distributive categories are discussed in
- Jeff Egger, The Frobenius relations meet linear distributivity, Theory and Applications of Categories, Vol. 24, 2010, No. 2, pp 25-38. (web)
Last revised on May 7, 2025 at 00:21:18. See the history of this page for a list of all contributions to it.